cara mengatasi laptop tidak bisa connect wifi windows 8
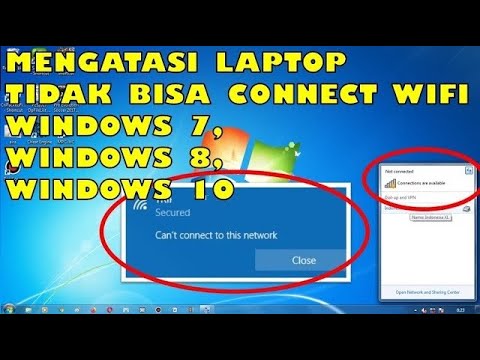
Title: Cara Mengatasi Laptop Tidak Bisa Connect Wifi Windows 10, 8 & 7
Channel: Jari Mungil Rayyan
Cara Mengatasi Laptop Tidak Bisa Connect Wifi Windows 10, 8 & 7 by Jari Mungil Rayyan
Windows 8 WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW!
Windows 8 Wireless Woes? Conquer Your Connection Conflicts!
Are you wrestling with WiFi woes on your Windows 8 machine? Does your once-reliable connection now resemble a temperamental toddler? You are not alone! Many users faced frustrating wireless internet problems. So, let's dive in and banish those connectivity headaches. We'll explore solutions to get you back online fast.
Decoding the WiFi Dilemma: Common Culprits and Clues
First, let's acknowledge the pain. A flaky WiFi connection can be profoundly annoying. Erratic disconnections, slow speeds, and an inability to even find your network can plague your experience. Therefore, understanding the potential causes is essential. Begin by asking yourself some questions. Has this problem started recently? Did you install any new software or hardware? Has anything else in your environment changed?
Consider your router. Is it functioning correctly? Sometimes, the issue stems from the router itself. Restarting your router can work wonders. It's the digital equivalent of a good night's sleep. Check the router's status lights. Do they indicate an internet connection? Also, verify your internet service provider hasn't experienced an outage. It is a possibility that the fault lies elsewhere.
Troubleshooting Tactics: Your Arsenal of Connectivity Solutions
Now, let's get tactical. We'll arm you with proven fixes. These steps should resolve most Windows 8 WiFi issues. The first step involves checking your network adapter drivers. Outdated drivers are a frequent culprit. They can cause conflicts and instability. Go to Device Manager, locate your network adapter, and update the driver. Download the newest driver from your adapter manufacturer’s website.
Subsequently, consider your network settings. Sometimes, a simple reset is all you need. Forget the network connection. Then, reconnect using your password. Windows 8 might have a glitch within its network profile. Doing so will refresh these settings. It often resolves connectivity issues.
Next, examine your power management settings. Windows 8 has power-saving features. These settings can inadvertently disable your wireless adapter. Access your network adapter properties in Device Manager. There should be a "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that allows Windows to turn off the adapter.
Advanced Maneuvers: Going Beyond the Basics
If the basic solutions fail, it's time to escalate. Let's try some advanced troubleshooting techniques. For instance, consider the interference factor. Wireless signals can be susceptible to interference. Other devices, like microwaves or cordless phones, can disrupt the signal. Moving your computer closer to the router can drastically improve the connection. Changing your router's wireless channel can help. Experiment with different channels. The goal is to find the least congested one.
Furthermore, investigate your security settings. WPA2 and WPA3 are the most secure protocols. Make sure your router uses one of these. An outdated or insecure protocol might be the source of the problem. It is crucial to strengthen your network’s security.
Consider a more dramatic approach: a system restore. This action will revert your system to a previous state. It's before the problem manifested. However, back up your essential files first. This safeguard precaution prevents data loss. If it works, the issue was likely caused by recent software modifications.
The Ultimate Victory: Reclaiming Your Wireless Freedom
After that, you'll hopefully have conquered your Windows 8 WiFi woes. You've navigated the troubleshooting maze. Now, you'll be enjoying smooth, stable connectivity. Remember to revisit these steps if issues reappear. Wireless technology can be fickle. Moreover, keep your drivers updated. Regularly update your router’s firmware. These proactive steps maintain optimal performance.
In conclusion, don’t let WiFi troubles disrupt your digital life. With the correct approach, you can overcome the challenges. Embrace the solutions we've discussed. If issues persist, seek professional help. Often, an expert can diagnose underlying problems. However, more often than not, you will be fine. Go forth and enjoy the freedom of a reliable wireless connection. Happy surfing!
Neighbor's WiFi: Secretly Steal Their Internet (Without Them Knowing!)Windows 8 WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW!
Ah, Windows 8. The operating system that, for many of us, felt like that experimental dish your eccentric Aunt Mildred insisted you try – fascinating, potentially disastrous, and leaving you with a lingering taste of… well, frustration, especially when it came to Wi-Fi. Remember those days? We do. The constant disconnections, the glacial loading speeds, the sheer panic when your connection dropped during a crucial online game or a video call? It was a collective nightmare. But fear not, fellow digital survivors! This isn't just a trip down memory lane; it's a comprehensive guide to conquering those Windows 8 Wi-Fi woes. So, buckle up, buttercups, because we're diving headfirst into the fixes!
1. The Windows 8 Wi-Fi Woes: A Trip Down Memory Lane
Let’s be honest, Windows 8 had its… quirks. While it brought some innovative features, the Wi-Fi connectivity often resembled a temperamental toddler – unpredictable and prone to tantrums. Remember the spinning “connecting” wheel that seemed to mock your desperate attempts at online access? It was enough to make even the most patient among us tear our hair out. We've all been there, smashing our laptops in frustration. But before we hurl our machines out of the window, and with hindsight being 20/20, let’s understand why Windows 8 gave us such a headache. Remember the early days of cloud computing? It wasn't exactly smooth sailing.
2. Identifying the Culprit: Is It Really Windows 8's Fault?
Before we start pointing fingers at Windows 8, let's perform a digital detective agency and rule out the other usual suspects. Your router? Perhaps. Your internet service provider (ISP)? Possibly. Your physical distance from the router? Definitely a factor. Think of your Wi-Fi signal as a radio wave – it’s easily disrupted by walls, metal objects, and even microwaves. Before we deep dive into Windows 8’s issues, let's eliminate these external factors. Consider starting at the source, and work your way to your device.
3. Restarting the Usual Suspects: The Power of a Reboot
This is the IT equivalent of “Have you tried turning it off and on again?” – a cliché, sure, but often surprisingly effective. Restart your computer, your router, and your modem. It's like hitting the reset button on a stressed-out brain. Often, these devices accumulate temporary glitches. A simple reboot can clear these out and restore your Wi-Fi connection to its former glory. It's the digital equivalent of taking a deep breath and starting fresh.
4. Driver Drama: The Root of Many Wi-Fi Troubles
Outdated or corrupted drivers are a common source of network problems. Think of drivers as the translators that allow your computer to understand and communicate with your Wi-Fi adapter. If the translator is broken or out of date, well, you can imagine the resulting communication breakdown. To update them, right-click on the Start button (or press Windows key + X) and select “Device Manager.” Expand the "Network Adapters" section, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and choose "Update driver." Follow the prompts, and hope for the best! It's like learning a new language – sometimes, it takes a few tries.
5. The Network Adapter Tango: Disabling and Re-enabling
Sometimes, the most straightforward solutions are the most effective. Head back to Device Manager, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and select "Disable." Wait a few seconds, then right-click it again and select "Enable." This simple act can sometimes reset the connection and restore your Wi-Fi to working order. It's a bit like giving your computer a playful nudge to get it back on track.
6. The Troubleshooter's Triumphs: Letting Windows Diagnose
Windows 8, despite its shortcomings, actually had a decent built-in troubleshooter. Right-click on the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray (the bottom-right corner) and choose "Troubleshoot problems." Let Windows do its magic. It will scan for common issues and attempt to fix them automatically. It’s like having a digital IT support person at your fingertips.
7. Static IP Adventures: A More Techy Solution
This is for the more tech-savvy among us. Sometimes, dynamic IP addresses can cause connectivity issues. Try assigning a static IP address to your computer. You'll need to access your router's settings to find the IP address range and gateway information. Then, go to Network Connections (search in the Start screen), right-click your Wi-Fi connection, select "Properties," and configure the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) settings to use a static IP address. This is a bit like giving your computer a permanent address on the internet.
8. Wireless Mode Mania: Exploring Your Router Settings
Your router’s wireless mode can affect your connection speed. Experiment with different modes (e.g., 802.11g, 802.11n, or 802.11ac if your router supports it) in your router’s settings. The optimal mode depends on your devices and your router's capabilities. This is like finding the perfect radio channel for your Wi-Fi signal.
9. Channel Surfing: Finding the Least Congested Frequency
Wi-Fi routers operate on different channels. If your channel is congested with other nearby Wi-Fi networks, your connection can be slow and unreliable. Access your router's settings and try switching to a less crowded channel. This is analogous to finding a less busy road to commute to work.
10. Firewall Fiddling: Ensuring Nothing Blocks Connections
Your firewall might be blocking your Wi-Fi connection. Check your firewall settings (search for "Windows Firewall" in the Start screen) and make sure your Wi-Fi network is allowed to communicate. This is like ensuring all the doors are open to receive your connection.
11. The DNS Dilemma: Switching to Public DNS Servers
Sometimes, your ISP's DNS servers can be slow or unreliable. Try switching to a public DNS server like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1). This can improve your browsing speed and resolve connection issues. It's like finding a faster postal service for internet requests.
12. Power Savings Panic: Disabling Power Management
Windows 8, in its quest for battery life, sometimes throttled Wi-Fi performance. In Device Manager (Network adapters, right-click your adapter, Properties, Power Management), uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This is crucial for desktop users, but a good idea for laptops too. It's like ensuring your Wi-Fi has enough juice to keep running.
13. Security Settings Shenanigans: Checking Your Encryption
Double-check your Wi-Fi security settings on your router. Ensure you're using a secure encryption method like WPA2 or WPA3 (if available). Avoid using WEP, as it's outdated and easily hackable. Think of this as selecting the safest lock for your Wi-Fi network.
14. System Restore Rescue: Rolling Back to a Stable State
If you’ve recently installed a program or made changes that might have caused your Wi-Fi problems, try using System Restore to revert to a previous state when your Wi-Fi was working correctly. It's like going back in time to fix a mistake.
15. The Ultimate Sacrifice: Reinstalling Wi-Fi Drivers (and Praying!)
As a last resort, and not always recommended, uninstall your Wi-Fi adapter drivers from Device Manager (right-click, uninstall), then restart your computer. Windows will often reinstall the drivers automatically. Alternatively, you can download the latest drivers from your computer manufacturer’s website and install them manually. Hope for the best (and maybe say a little prayer!). It's a digital Hail Mary, hoping for a miraculous fix.
The Final Connection: Conquering the Windows 8 Wi-Fi Nightmare!
So, there you have it – a comprehensive guide to conquering the Windows 8 Wi-Fi nightmare. We’ve covered everything from the simple reboot to the more complex driver updates and settings tweaks. Remember, troubleshooting Wi-Fi issues is like solving a puzzle. It takes patience, persistence, and a bit of trial and error. Don't get discouraged if the first few steps don't work. Keep experimenting. We hope these solutions have helped you regain control of your internet connection and reclaim some sanity from the sometimes-chaotic world of Windows 8. Go forth and conquer! Now, go enjoy the internet without the rage!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. My Wi-Fi connection keeps dropping. What should I do first?
Restart your computer, router, and modem. It's the digital equivalent of "have you tried turning it off and on again?" Also, check your physical distance from the router and look for potential obstructions.
2. How do I update my Wi-Fi drivers?
Right-click the Start button, select "Device Manager," expand "Network Adapters," right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and choose "Update driver." Follow the prompts.
3. What's the difference between WPA, WPA2, and WEP security?
WEP is outdated and
Laptop WiFi Vanished? Find Your Network NOW!Cara atasi WiFi tidak bisa connect di laptop not connected
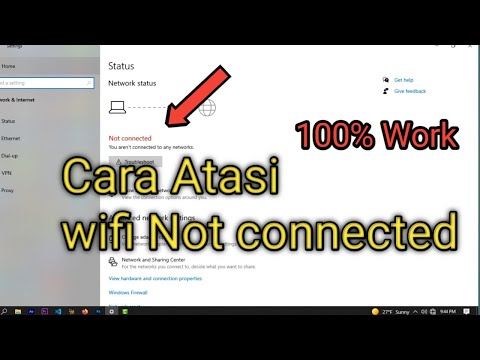
By ijal tutorial Cara atasi WiFi tidak bisa connect di laptop not connected by ijal tutorial
Cara Mengatasi Wifi Laptop Tidak Bisa di Aktifkan Windows 8

By LAPTOP TUTORIAL Cara Mengatasi Wifi Laptop Tidak Bisa di Aktifkan Windows 8 by LAPTOP TUTORIAL
Cara mengaktifkan wifi di windows 8
By AW Tutorial Cara mengaktifkan wifi di windows 8 by AW Tutorial

Title: Sinyal Wifi Laptop Hilang Ada Tanda Silang Merah Ini Solusi Singkatnya
Channel: Gadget NoteIn
Sinyal Wifi Laptop Hilang Ada Tanda Silang Merah Ini Solusi Singkatnya by Gadget NoteIn
Change Wifi Settings
Windows 8 WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW! Your Comprehensive Guide to Wireless Stability
Is your Windows 8 machine plagued by frustrating WiFi connectivity issues? Do you find yourself constantly battling dropped connections, slow speeds, or an inability to even connect to your network? You're not alone. Countless users have experienced the same WiFi woes under Windows 8. We understand your frustration, and we're here to help. This guide will walk you through a series of proven solutions, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to banish those WiFi nightmares and reclaim your seamless wireless experience. Forget endless troubleshooting forums and generic advice; we're diving deep to provide you with the specific, actionable steps you need to get back online, and stay online.
Understanding the Root of the Problem: Common Windows 8 WiFi Issues
Before we jump into the fixes, let's briefly identify the common culprits behind WiFi problems in Windows 8. Pinpointing the source of your issues is the first step toward a lasting solution. These problems can stem from a variety of sources: outdated or corrupted drivers, incompatible network settings, power management conflicts, and even hardware limitations. Let's look at each of these.
One of the primary causes of WiFi instability in Windows 8 is outdated or incompatible network adapter drivers. These drivers are the software that allows your computer to communicate with your wireless adapter. An outdated driver can lead to a host of problems, including intermittent connectivity, slow speeds, and complete failure to connect. Similarly, a corrupted driver can wreak havoc on your network performance, causing the same frustrating issues.
Another common culprit is incorrect network configuration. Windows 8 has various settings that affect how your machine interacts with your WiFi network. Incorrect settings, such as those related to IPv4 or IPv6 addressing, can lead to connection failures or slow speeds. The protocol settings can cause network problems as well, which are explained in further sections.
Power management settings also play a crucial role in WiFi stability. Windows 8, by default, is configured to conserve power. While this is beneficial for battery life, it can sometimes interfere with your WiFi adapter’s performance. Aggressive power-saving measures can cause your adapter to shut down or reduce its performance, leading to dropped connections or slow speeds.
Finally, hardware limitations can occasionally contribute to WiFi problems. Older wireless adapters may not support the latest WiFi standards, such as 802.11ac, resulting in slower speeds and decreased range. The router you use could be a problem as well.
Step-by-Step Solutions: Fixing Your Windows 8 WiFi Problems
Now, let's get to the good part: the solutions. Follow these steps systematically, testing your WiFi connection after each one. We'll start with the simplest solutions and progress towards more complex ones.
1. Driver Updates: The Foundation of a Stable Connection
This should be the first check you make. Updating your network adapter drivers is the single most impactful step you can take to resolve WiFi issues. Outdated drivers are a frequent cause of wireless problems.
- Automatic Driver Update: Windows 8 has a built-in driver update tool. To use it, navigate to the Device Manager. You can access the Device Manager by right-clicking on the Start button and selecting it from the menu. In the Device Manager, expand the "Network adapters" category. Right-click on your wireless adapter (the name will vary, but it will typically include "Wireless" or "WiFi") and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows will then search for and install the latest drivers available.
- Manual Driver Update: If the automatic update doesn't find the latest drivers, you can try manually updating them. Visit the website of the manufacturer of your network adapter. Common manufacturers include Intel, Realtek, and Broadcom. Download the latest drivers specific to your Windows 8 operating system. Once downloaded, run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Driver Rollback: If a recent driver update caused the problem, you can roll back to a previous version. In the Device Manager, right-click on your wireless adapter and select "Properties." Go to the "Driver" tab. If the "Roll Back Driver" button is available, click it. Follow the instructions to revert to the previous driver version.
2. Network Adapter Power Management Tweaks
Power management settings can negatively impact WiFi performance. Adjust these settings to prevent your adapter from being unexpectedly shut down.
- Disable Power Saving: In the Device Manager (as above), right-click your wireless adapter and select "Properties." Go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." Click "OK."
3. Optimizing Network Adapter Settings
Fine-tuning your network adapter's advanced settings can sometimes resolve connectivity issues. These settings control how your wireless adapter communicates with your router.
- Access Advanced Settings: In the Device Manager, right-click your wireless adapter, select "Properties," and go to the "Advanced" tab. The available options will vary depending on your adapter.
- Key Settings to Adjust:
- Wireless Mode: Try setting this to a specific mode (e.g., 802.11g or 802.11n) instead of "Auto." Experiment with different modes.
- 802.11n Channel Width: If available, set this to "20 MHz" or "20/40 MHz" depending on your router's capabilities.
- Roaming Aggressiveness: Try setting this to "Medium" or "Low." This controls how aggressively your adapter searches for stronger WiFi signals.
- Transmit Power: set this to the Highest setting.
4. Resetting Your Network Configuration
Sometimes, your network settings become corrupted, leading to connectivity problems. Resetting these settings can often resolve the issue.
- Run the Network Troubleshooter: Windows 8 has a built-in network troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common network problems. Right-click on the network icon in the system tray (usually near the clock) and select "Troubleshoot problems." Follow the on-screen instructions.
- Reset TCP/IP Stack: Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each one:
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip reset- Restart your computer after running these commands.
5. Router Configuration Considerations
Your router's settings also play a vital role in WiFi performance. Ensure your router is configured correctly to avoid connectivity problems.
- Router Firmware Update: Outdated router firmware can cause compatibility issues. Check your router manufacturer's website for firmware updates. Download and install the latest firmware for your router model.
- Channel Selection: WiFi signals operate on different channels. Overcrowded channels can lead to interference and slow speeds. Log into your router's configuration page (usually by typing your router's IP address in your web browser). In the wireless settings, look for the "Channel" option. Try changing the channel to a less congested one. You can use a WiFi analyzer app (available for smartphones and other devices) to determine the least crowded channels in your area. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are generally recommended as they overlap less.
- Security Protocols: Ensure your router uses a secure security protocol like WPA2 or WPA3. Avoid using WEP, as it is outdated and insecure.
6. Addressing IPv6 Issues – A Deep Dive
While not as common as other issues, problems with IPv6 can sometimes lead to WiFi connectivity problems. Some users have reported that disabling IPv6 resolved their problems under Windows 8.
- Disabling IPv6: Open "Network Connections" (search for it in the Windows search bar). Right-click on your WiFi connection and select "Properties." In the list, uncheck the box next to "Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)." Click "OK." Test your connection after making this change. (Note: Disable IPv6 only if you are certain it’s not required for your other internet services.)
7. Hardware Considerations
In some cases, hardware issues can contribute to WiFi problems. These are less frequent, but it's worth considering.
- Wireless Adapter Hardware Check: If you've tried all the previous steps and are still experiencing problems, it's possible your wireless adapter is failing. Try using a different wireless adapter (if possible) to see if that resolves the issue.
- Router Placement: Ensure your router is positioned in a central location away from obstructions like walls and metal objects that can interfere with the WiFi signal.
8. Windows Firewall Interference
The Windows Firewall might sometimes block network connections.
- Check Firewall Settings: Access the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security through the search bar. Ensure that the necessary network connections and rules for the applications you use are enabled.
Troubleshooting Tips for Persistent Problems
Even after following these steps, you may still encounter occasional WiFi issues. Here are some additional troubleshooting tips to help you diagnose and resolve persistent problems:
- Restart Your Router and Modem: This simple step often resolves many WiFi issues. Unplug your router and modem from their power sources, wait for 30 seconds, plug the modem back in, wait for it to boot up, and then plug the router back in and wait for it to boot.
- Check Your Internet Service Provider (ISP): If you're still having trouble, contact your
