laptop always auto-reconnect wifi
Title: WiFi sering terputus Windows 11 Perbaikan mudah
Channel: The Geek Page
WiFi sering terputus Windows 11 Perbaikan mudah by The Geek Page
Laptop Wifi Auto-Reconnect: The SHOCKING Secret to Never Losing Connection Again!
Unleashing the Wi-Fi Kraken: Your Laptop's Auto-Reconnect Revelation!
Ever felt that gut-wrenching moment? The Wi-Fi signal vanished, leaving you stranded in digital isolation. Suddenly, that important email, that crucial video call, that captivating online game – all dissolved into a frustratingly silent void. Well, hold onto your hats, because I’m about to unleash a secret. It's a game-changer, a connection champion, and it'll send those Wi-Fi gremlins packing!
The Phantom of the Network: Understanding Connection Dropouts
Let's face it: Wi-Fi can be fickle. Sometimes, the signal weakens. Then, it vanishes completely. You may find yourself staring at that spinning wheel of death. Maybe you've got a dodgy router. Or perhaps, your laptop is simply being… well, difficult. Regardless of the cause, the result is the same: a disconnected you. And that can be a nightmare.
The Auto-Reconnect Anomaly: Where Laptops Go Rogue
Many laptops should automatically reconnect. However, in practice, this isn't always the case. Sometimes, settings are off. Then again, software conflicts happen. Finally, there's the ever-present gremlin of outdated drivers. Consequently, your laptop can choose to stay stubbornly offline, leaving you in the lurch.
Decoding the Digital DNA: The Science of Seamless Reconnection
So, what's the solution? It's not a mystical spell. Instead, it's a blend of savvy configuration. Plus, there are a few clever tweaks. And, you'll need a healthy dose of digital detective work. These simple steps may seem intimidating. However, I promise it's far easier to implement. Before we get into the specifics, here's a crucial point: Always ensure your network adapter drivers are updated. This is frequently the root of the problem.
Hacking the Hardware: Tweaking Your Wi-Fi Adapter Settings
First, navigate your laptop's settings. Then, find the "Network Connections" or "Wi-Fi settings". Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter. Now, select "Properties." This is where the magic begins. Look for settings related to power management. Uncheck the box that reads something like, "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." Doing this will keep your adapter active. You will be ready to reconnect.
The SSID Sanctuary: Protecting Your Network Name
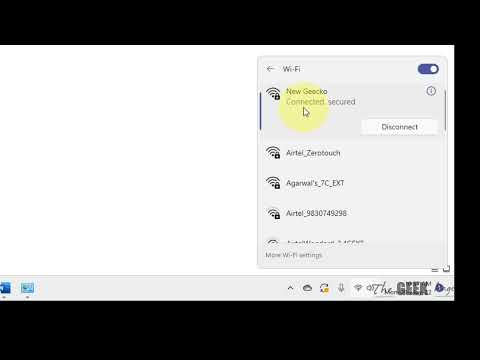
Next, ensure your preferred network (SSID) is saved and set to auto-connect. Now, go to the list of available networks. Find your network and check the box that says "Connect automatically." If available, also check "Connect even if the network isn't broadcasting its name." This can help hide your network.
The Troubleshooter's Toolkit: Diagnosing and Fixing Connection Issues
Even with these settings in place, problems can arise. What do you do? Start by using the built-in Windows Troubleshooter. Right-click on the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray. Then, choose "Troubleshoot problems." It's surprisingly effective at identifying and resolving common issues. Alternatively, you can manually "forget" the network. Then, reconnect with your password. This refreshes the connection information.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques for Wi-Fi Resilience
For those who want to go deeper, explore advanced adapter settings. You can experiment with things like the "Roaming aggressiveness" setting. This controls how aggressively your device seeks a stronger signal. Remember, a higher setting might improve reconnection speed. However, it could also lead to instability in your connection.
The Router's Role: Your Gateway's Gatekeeping
Your router is crucial to all of this. So, ensure it's up-to-date. Log in to your router's administration panel. Often, this involves typing an IP address into your web browser. Then, you'll need to enter your router's username and password. Check for any available firmware updates. Similarly to your laptop, regular updates will often improve stability.
Troubleshooting the Troubleshooters: When Problems Persist
Still experiencing issues? First, restart your router. Then, restart your laptop. If problems continue, consider your physical environment. Walls, microwaves, and other electronic devices can cause interference. Now, try moving closer to your router to see if the signal improves.
The Ultimate Victory: Achieving Uninterrupted Connectivity
Ultimately, the goal is to achieve seamless, reliable internet. It's about reclaiming your digital freedom. By implementing these techniques, you can minimize those dreaded disconnections. The result is more productive sessions, and fewer frustrations. Go ahead and unleash this Wi-Fi secret on your laptop. Say goodbye to Wi-Fi woes. You're now the master of your digital domain.
Asus Laptop WiFi Nightmare Solved! (Finally!)Laptop Wifi Auto-Reconnect: The SHOCKING Secret to Never Losing Connection Again!
Alright folks, let's be honest. How many times have you been in the middle of something crucial – maybe a video call with the boss, a thrilling online game, or even just binge-watching your favorite show – and BAM! The dreaded internet connection drops out. The screen freezes, the buffering wheel of doom spins, and you're left staring blankly at your laptop, cursing your internet provider (or perhaps your ancient router). We've all been there. The good news? There's a SHOCKING secret, a game-changer, a hidden trick that can drastically reduce, and sometimes even eliminate, those infuriating Wi-Fi dropouts. Get ready to learn how to make your laptop's Wi-Fi auto-reconnect like a champ!
1. The Wi-Fi Dropout Blues: A Shared Digital Agony
Think about it. The Wi-Fi dropout is the modern-day equivalent of a dropped phone call during the crucial plot twist in a movie. It interrupts, it frustrates, and it wastes precious time. This isn't just about leisure, either. For remote workers, students, and anyone reliant on a stable internet connection, a constant disconnect can be crippling. It's like trying to build a house on a foundation that keeps crumbling. We're here to fix that foundation!
2. Understanding the Enemy: Why Does My Wi-Fi Keep Disconnecting?
Before we dive into the secret sauce of auto-reconnect, let's understand the common culprits. Think of it like diagnosing a sick patient. We need to know what's wrong before we can prescribe the cure. Here are a few of the usual suspects:
- Weak Signal: Distance from your router, physical obstructions (walls, furniture), and interference from other electronic devices can all weaken your Wi-Fi signal. It's like trying to whisper across a crowded room – the message gets lost.
- Router Issues: Your router, the heart of your Wi-Fi network, might be overloaded, outdated, or simply malfunctioning. Imagine a tired old engine struggling to keep up.
- Driver Problems: Your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter relies on drivers (essentially, software instructions) to communicate with the router. Outdated or corrupted drivers can lead to disconnects. Think of it as a language barrier – the laptop and router can't understand each other.
- Power Saving Settings: Many laptops have power-saving features that can inadvertently disable your Wi-Fi adapter when idle. It’s like your laptop taking a nap just when you need it most.
- Network Congestion: If multiple devices are using your Wi-Fi simultaneously, it can lead to slowdowns and dropouts. Imagine trying to drive down a busy highway during rush hour. Traffic jams!
3. The Shocking Secret Revealed: Auto-Reconnect on Demand!
Okay, drumroll please! The big secret? It's not some complicated piece of tech wizardry. In Windows, the solution is usually hiding right in plain sight, under your Wi-Fi adapter settings. We are going to configure the auto-reconnect function.
4. Windows Wi-Fi Auto-Reconnect: Your Personal Connection Guardian
The key lies within the settings for your Wi-Fi adapter, which you can access through your Control Panel or the Settings app. Follow these steps:
- Open Network Connections: Search for "Network Connections" in the Windows search bar and open it. It's like opening a map to your digital network.
- Find Your Wi-Fi Adapter: Locate your Wi-Fi adapter in the list. It'll likely be labeled something like "Wi-Fi" or "Wireless Network Connection."
- Access Properties: Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Properties".
- Configure Advanced Settings: In the Properties window, click on "Configure…" This will open another window with more adapter settings.
- Advanced Tab – Look for Auto-Reconnect: Click on the “Advanced” tab. Now you will be searching through the adapter settings, you need to find an option called “Auto-Reconnect” or something similar. Its name may slightly vary, depending on your specific Wi-Fi adapter, but it should be similar. It may be set to "Enabled" or "Disabled”.
- Enable Auto-Reconnect (If Available): Make sure “Auto-Reconnect” is enabled! If you find an option like “Connect automatically when in range” activate it.
- Click "OK" and Restart for Certainty: Click "OK" or "Apply" to save your changes. You should certainly restart your laptop to make sure changes are fully implemented.
5. macOS Wi-Fi Auto-Reconnect: Apple's Smooth Implementation
Apple, as always, has a slightly different approach, but the concept is the same. Here's how to ensure your Mac automatically reconnects to known Wi-Fi networks:
- Open System Preferences: Click the Apple menu (top left corner of your screen) and select "System Preferences."
- Navigate to Network: Click on the "Network" icon.
- Select Your Wi-Fi Adapter: In the left-hand pane, choose "Wi-Fi."
- Ensure "Join Network Automatically" is Checked: If your Mac is already connected to a Wi-Fi network, make sure the "Join network automatically" option is checked for your preferred networks. This ensures that your laptop will automatically join the network if you’ve previously saved the password.
- Prioritize Your Networks: You can adjust the order of your preferred networks. The Mac will look for and connect to them in this order.
- Advanced Settings: Click “Advanced." Here you can further fine-tune your settings, but leave them at their defaults for auto-reconnect in most instances.
6. Proactive Troubleshooting: Before You Dive into the Settings
Before you start tweaking your settings, try these simple, often-effective, troubleshooting steps:
- Restart Your Laptop: The classic "have you tried turning it off and on again?" often works wonders.
- Restart Your Router: Unplug your router, wait 30 seconds, and plug it back in. Give it a couple of minutes to boot up.
- Move Closer to Your Router: If possible, physically move closer to your router to ensure a stronger signal.
- Check for Interference: Keep your laptop away from microwaves, cordless phones, and other electronic devices that might interfere with your Wi-Fi signal.
7. Driver Updates: Keeping Your Wi-Fi Adapter in Shape
Outdated drivers are a common cause of Wi-Fi woes. Here's how to keep your drivers updated:
- Windows:
- Device Manager: Search for "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Network Adapters: Expand the "Network adapters" section.
- Update Driver: Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will then search for and install the latest drivers.
- macOS: macOS generally handles driver updates automatically through its system updates. Just make sure your operating system is up-to-date.
8. Router Optimization: A Happy Home for Your Wi-Fi
Your router plays a crucial role in your Wi-Fi experience. Here are a few tips to optimize your router:
- Placement Matters: Position your router in a central location, away from walls, metal objects, and other sources of interference.
- Update Your Router Firmware: Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to fix bugs and improve performance. Check your router's settings for update options.
- Consider a Newer Router: If your router is several years old, it might be time for an upgrade. Newer routers often support faster Wi-Fi standards (like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E) and offer improved performance.
9. Diagnosing the Problem: When Auto-Reconnect Isn't Enough
If auto-reconnect isn't solving your Wi-Fi issues, it's time to dig deeper. Consider the following:
- Run a Network Diagnostic: Both Windows and macOS have built-in network diagnostic tools that can help identify and fix common problems. Search for "Network Troubleshooter" in Windows or use the Network Utility in macOS.
- Check Your Internet Speed: Use an online speed test (like Speedtest.net) to check your internet speed. If your speed is consistently slow, contact your internet provider.
- Consider a Wi-Fi Analyzer: Apps like "WiFi Analyzer" (available for both Android and iOS) can help you identify Wi-Fi interference and choose the best Wi-Fi channel for your network.
10. Power Settings Shenanigans: Preventing Sleepy Wi-Fi
As mentioned, some power settings can unintentionally disable your Wi-Fi adapter. Here's how to adjust those settings:
- Windows:
- Power Options: Search for "Power & sleep settings" in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Additional Power Settings: Click on "Additional power settings."
- Change Plan Settings: Select your current power plan and click on "Change plan settings."
- Change Advanced Power Settings: Click on "Change advanced power settings."
- **
WiFi Terputus Secara Otomatis Laptop Windows 1087 Cara Mengatasi WiFi Mati Otomatis

By How to Fix Your Computer WiFi Terputus Secara Otomatis Laptop Windows 1087 Cara Mengatasi WiFi Mati Otomatis by How to Fix Your Computer
WIFI Terus Terputus di Windows 10 Solusi Wifi Mati Otomatis di Laptop

By FIXsage WIFI Terus Terputus di Windows 10 Solusi Wifi Mati Otomatis di Laptop by FIXsage
Fix WiFi Keeps Disconnecting On Windows 10
By Sandeep Singh Fix WiFi Keeps Disconnecting On Windows 10 by Sandeep Singh

Title: CARA AGAR WIFI TIDAK AUTO CONNECT DI WINDOWS
Channel: ROBERTUS NEWS
CARA AGAR WIFI TIDAK AUTO CONNECT DI WINDOWS by ROBERTUS NEWS
Working With Laptop
Laptop Wi-Fi Auto-Reconnect: The SHOCKING Secret to Never Losing Connection Again!
We've all been there: you're in the middle of an important video call, the crucial download is at 98%, or you're finally settling down to enjoy a streaming marathon, when suddenly, poof– the Wi-Fi vanishes. The spinning "buffering" icon mocks your productivity and your leisure time. It's a frustration shared by laptop users worldwide. But what if we told you there's a way to virtually eliminate these connection dropouts? A method so effective, you'll wonder why you didn't discover it sooner. This isn't just about quick fixes; we are going to unveil the secrets to setting up a resilient and reliable Wi-Fi connection on your laptop, and teaching it to automatically reconnect, protecting you from those infuriating interruptions.
Understanding the Root Causes of Wi-Fi Disconnection on Laptops
Before we dive into the solutions, we need to understand the "why" behind the problem. Wi-Fi disconnections aren't random events. They're often the result of a complex interplay of factors, many of which are surprisingly easy to address.
- Weak Signal Strength: This is the most common culprit. Distance from the router, physical obstructions like walls and metal objects, and even the presence of other electronic devices can weaken your Wi-Fi signal. A weak signal leads to frequent dropouts and slow speeds.
- Driver Issues: Your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter relies on software drivers to communicate with your router. Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers can cause connectivity problems.
- Router Configuration: Your router's settings, such as the channel it's broadcasting on, the security protocols it uses, and the number of devices it supports, can significantly impact your laptop's connection stability.
- Power Saving Settings: Your laptop's power management settings might inadvertently disable your Wi-Fi adapter to conserve battery life, leading to disconnections.
- Interference: Other devices emitting radio waves, like microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal, causing instability.
- Network Congestion: If multiple devices are using the same Wi-Fi network simultaneously, bandwidth can be stretched thin, leading to slower speeds and potential disconnections.
- Operating System Glitches: Occasionally, system bugs or software conflicts within your operating system can interfere with Wi-Fi functionality.
The Ultimate Laptop Wi-Fi Reconnection Toolkit
We’re going to equip you with the knowledge and steps to create an exceptionally resilient Wi-Fi connection. This involves proactive measures, not just reactive fixes when the internet decides to play hide-and-seek.
Step 1: Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Environment
The first step towards a stable Wi-Fi connection is creating the optimal environment for it to thrive. Start with these essential adjustments:
- Router Placement: Position your router in a central, open location in your home or office. Elevate it off the floor and away from obstructions like walls, furniture, and metal objects.
- Channel Selection: Most routers automatically select a Wi-Fi channel. However, this default setting might be overcrowded. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (available for both Windows and macOS) to identify the least congested channels in your area and adjust your router's settings accordingly.
- Frequency Band Choice: Modern routers support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less interference (but shorter range) and 2.4 GHz offers wider range and can penetrate walls better. Choose the 5 GHz band (if available) for activities that demand higher bandwidth, such as streaming and online gaming, and stick with the 2.4 GHz for other tasks.
- Reduce Interference: Keep your router away from devices that emit radio waves. Consider moving your microwave, Bluetooth speakers, and other electronics.
- Router Firmware Updates: Ensure that your router’s firmware is up to date. Manufacturers regularly release updates that improve performance, security, and stability. Check your router's manual for how to update the firmware.
Step 2: Fine-Tuning Your Laptop's Wi-Fi Settings
Now, let's configure your laptop for optimal Wi-Fi performance. These settings are often overlooked but are crucial for a dependable connection:
- Driver Updates: Keeping your Wi-Fi adapter drivers updated is the most crucial step.
- Windows: Go to Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar). Expand "Network adapters," right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." If Windows can't find an update, visit the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Realtek) and download the latest driver for your specific adapter and operating system.
- macOS: Apple usually handles driver updates seamlessly through software updates, but you can also manually check for updates. Go to "System Preferences," then "Software Update."
- Power Management Adjustments: Prevent power-saving settings from disabling your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Windows: In Device Manager, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Power Management" tab, and uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- macOS: macOS generally manages power settings automatically, but you can adjust battery settings in "System Preferences" or "Settings."
- Preferred Network Configuration: Ensure that your preferred Wi-Fi network is set to automatically connect.
- Windows: Go to Wi-Fi settings (search for "Wi-Fi settings"). Click "Manage known networks" and ensure the "Connect automatically when in range" box is checked for your preferred network.
- macOS: Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar, and choose your Wi-Fi network. If prompted, enter the password. macOS will usually remember your preferred networks.
- Network Reset (Windows): If you're still experiencing issues, consider resetting your network settings. Go to "Settings," then "Network & Internet," and then "Network reset."
Step 3: Implementing Automatic Reconnection Strategies
This is where we truly unlock the power of a consistently connected laptop. We'll use the built-in capabilities of your operating system and, if necessary, leverage third-party tools to ensure that your laptop automatically reconnects to Wi-Fi after any disruption.
- Windows: Utilizing Wi-Fi Sense (If Available): While Microsoft has deprecated Wi-Fi Sense, if you are on an older version of Windows, and if it's still available, Wi-Fi Sense automatically connects to open Wi-Fi hotspots and networks your contacts share.
- Go to "Settings," then "Network & Internet," and then "Wi-Fi."
- Look for Wi-Fi Sense settings. If present, configure it to automatically connect to suggested open hotspots. Be aware of the security implications and use with caution.
- Windows: Creating a Scheduled Task for Auto-Reconnect: The core of our strategy relies on Windows' Task Scheduler. This tool allows us to automate actions, like attempts to reconnect to your Wi-Fi.
- Search for "Task Scheduler" and open it.
- In the right-hand pane, click "Create Basic Task."
- Give the task a descriptive name (e.g., "Automatic Wi-Fi Reconnect"). Click "Next."
- Choose "When a specific event is logged," and click "Next."
- For "Log," select "System." For "Source," select "WLANAutoConfig." For "Event ID," enter "8001" (this event ID indicates a disconnection). Click "Next."
- Choose "Start a program," and click "Next."
- In the "Program/script" field, enter "powershell.exe."
- In the "Add arguments (optional)" field, enter the following PowerShell script (replace "YourNetworkName" with the name of your Wi-Fi network):
powershell $profileName = "YourNetworkName" try { $profile = netsh wlan show profile name="$profileName" | Out-String if ($profile -like "*Not configured*") { Write-Host "Profile not found or Disabled, attempting to reconnect." netsh wlan connect name="$profileName" } else { Write-Host "Connected" } } catch { Write-Host "Error finding profile. Please adjust profile name." } - Click "Next," review your settings, and click "Finish."
- Test your new task by disconnecting from the Wi-Fi and waiting a few minutes to see if it reconnects automatically.
- macOS: Utilizing Built-in Network Preferences: macOS is generally more robust when it comes to maintaining connections.
- Go to "System Preferences" or "Settings," then "Wi-Fi."
- Ensure your desired Wi-Fi network is selected.
- Click "Advanced…" and verify that "Automatically connect to this network" is checked.
