laptop cannot connect to 2.4 ghz wifi

Title: How to enable 2.4 GHz wifi band on laptop
Channel: TechEpu
How to enable 2.4 GHz wifi band on laptop by TechEpu
laptop cannot connect to 2.4 ghz wifi, laptop not connecting to 2.4 ghz wifi, can't connect to 2.4ghz wifi pc, why i cannot connect to 2.4ghz wifi
Laptop Refuses 2.4GHz WiFi? This SHOCKING Fix Works!
My Laptop's 2.4GHz WiFi Woes: A Tech Odyssey
Have you ever stared at your screen, heart sinking, as your laptop stubbornly refuses to connect to your 2.4GHz WiFi network? It's a frustrating experience, to say the least. Because let's face it, we rely on seamless connectivity. And, the inability to join your network can feel like a digital roadblock. However, before you toss your laptop out the window, there's hope! I faced this very issue. And after a lot of head-scratching and troubleshooting, I found a solution. It's a solution that might just save your sanity.
The Mysterious Case of the Missing WiFi
The scenario likely sounds familiar. You’re eager to work or stream. But your laptop only sees the faster 5GHz network. Sadly, the 2.4GHz, the one that seems to have vanished, is nowhere in sight. This is puzzling! So, what gives? Well, let’s dive into the rabbit hole of potential culprits.
One common reason is a simple glitch. Your laptop or router might be undergoing a temporary hiccup. In these cases, a quick reset might restore everything. But, in other cases, the fix isn't so obvious. Keep reading, because more troubleshooting might be necessary.
Troubleshooting 2.4GHz WiFi: Initial Steps
First things first, let's run through some basic checks. These are often the easiest fixes. They are also the ones you should test first.
- Restart Everything: Power cycle your router and your laptop. Then let both devices fully reboot. Sometimes, this seemingly simple step is all that's needed. However, if it doesn't work, don't panic.
- Check the Router's Configuration: Ensure the 2.4GHz band is enabled. Some routers allow you to turn off specific bands. Therefore, check your router's admin panel. Furthermore, double-check the settings to confirm it is broadcasting. Because, it's a common oversight.
- Driver Updates: Your laptop's WiFi adapter needs up-to-date drivers. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues. Therefore, visit your laptop manufacturer's website. After that, download and install the latest drivers for your network adapter.
Deeper Dive: Advanced Troubleshooting
If those initial steps fail, we need to dig a little deeper. Thus, here are some more advanced troubleshooting steps.
- Channel Overlap: The 2.4GHz band has limited channels. Other nearby WiFi networks can interfere. To mitigate this, access your router's settings. Then change the 2.4GHz channel. Experiment with channels 1, 6, and 11. Thus, this is because they are the least likely to overlap.
- Wireless Mode Settings: Your router's wireless mode can impact compatibility. So, ensure your router supports the 802.11b/g/n standards. In addition, check your router's configuration. If the settings aren't appropriate, change the settings.
- Interference is the Enemy: In the 2.4GHz band, interference is common. This can come from various sources. Things like microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even other electronic gadgets can cause interference. Thus, minimize these devices' proximity to your laptop and router. Test to see if this affects the laptop's network.
The Shocking Fix: A Hidden Gem
Sometimes, the solution lies in the obscure. After extensive research and trial and error, I found one specific fix worked perfectly. However, it’s not a magic bullet for every situation. Nevertheless, it's worth trying. What I'm talking about is the "Channel Width" setting.
The 2.4 GHz band has a channel width setting. It can sometimes be set to a specific value which is causing problems. Therefore, in your router's settings, look for the "Channel Width" or "Bandwidth" option.
- Experiment with Settings: Try changing the channel width. Most of the time, the ideal setting is 20MHz. Test and see if this fixes the problem. After you apply these changes, reboot your router. After the router reboots, test your laptop's WiFi connection.
When All Else Fails: Seeking Professional Help
If you've tried everything but still can't connect, consider professional help. There might be a hardware issue with your laptop's WiFi adapter. Or, there might be a complex network problem. A tech support specialist can help you with further troubleshooting.
Final Thoughts and a Dash of Hope
Facing WiFi problems can be extremely frustrating. But don't lose hope. Usually, there's a solution. By methodically working through troubleshooting steps, you'll be back online. Moreover, you'll likely be able to connect to your 2.4GHz network again. Remember, technology can be tricky. But also remember that there is always a solution. So take a deep breath, try these fixes, and get back to what matters most.
Laptop WiFi Nightmare? This 1-Minute Fix Will SHOCK You!Laptop Refuses 2.4GHz WiFi? This SHOCKING Fix Works!
Hey there, fellow tech-wielders! Ever find yourself staring at your laptop, utterly bewildered, as it stubbornly refuses to connect to your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi network? The frustration is all too real, right? I remember a time when my own laptop, "Betsy," (yes, I name my tech – don’t judge!) decided it had a sudden aversion to the slower, yet often more reliable, 2.4GHz band. It was like she was saying, "Nah, 5GHz or bust!" And in the vast digital landscape, that’s a huge pain, especially if you're in a location with spotty 5GHz coverage or a lot of interference. We've all been there. But don't despair! We're going to dive deep into the frustrating world of 2.4GHz WiFi woes and, more importantly, reveal a SHOCKING fix that actually works.
Why Is My Laptop Ignoring 2.4GHz WiFi? Decoding the Digital Drama
First off, let’s get to the bottom of this digital drama. Why does your laptop suddenly turn its nose up at the trusty 2.4GHz frequency? It's like your laptop is having a dramatic moment, throwing shade at the less glamorous network option. There are several potential culprits, each with its own personality and level of annoyance. Think of these as the suspects in our Wi-Fi whodunnit.
Driver Dilemma: Outdated, corrupted, or simply incompatible Wi-Fi drivers are a huge suspect. This is often the first place to start. It's like your laptop is trying to speak a language it no longer understands.
Hidden Network Hangups: Believe it or not, a hidden network name (SSID) can sometimes cause problems. This is like trying to find a secret club that's only accessible through a secret knock.
Router Rage: Your router, the gatekeeper of your internet, might be misconfigured or having a temper tantrum of its own. Think of it as the grumpy neighbour who occasionally cuts off your access.
Channel Chaos: The 2.4GHz band is pretty crowded. If your router is set to an overlapping channel, you're essentially competing with your neighbors for bandwidth, creating digital gridlock.
Laptop’s Limitations: Older laptops sometimes have hardware limitations that make them not very friendly to the 2.4GHz band. It's like expecting a vintage car to keep up with a Formula 1 race.
Security Snafus: Incorrect security settings on your router, or a mismatch between your laptop's and router's security protocols, can create a roadblock.
The Symptoms: Clues That Something's Amiss
Before we jump into solutions, let's identify the telltale signs that your laptop is indeed ignoring the 2.4GHz band. Are you seeing these symptoms? If so, then we're on the right track:
- The Invisible Network: Your laptop simply doesn't see the 2.4GHz network when scanning for available Wi-Fi connections. It's as if it's been erased from existence!
- Weak or Unstable Connection: If it does see the network, but the connection is weak, unstable, or constantly dropping, that’s another red flag.
- Error Messages Galore: Pop-up messages like "Unable to connect" or "Cannot connect to this network" are your laptop’s way of screaming for help.
- 5GHz Works Fine: Ironically, your laptop might connect flawlessly to your 5GHz network, emphasizing the 2.4GHz banishment.
Step-by-Step: Unveiling the SHOCKING Fix!
Okay, are you ready for the big reveal? The SHOCKING fix we will dive into is not a single, magic button, but a combination of several potential solutions, like a chef who chooses the right ingredients for the perfect flavor. We're going to walk through these steps with you, ensuring the best chances of restoring your laptop's connection to the 2.4GHz band.
Driver Detective Work: This is the first step.
- Go to your laptop's manufacturer’s website (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo).
- Find the "Support" or "Drivers" section.
- Enter your laptop's model number to locate the correct Wi-Fi drivers.
- Download and install the latest driver available. Think of it as a software update – it’s constantly being refined.
- Restart your laptop. This allows the changes to take effect.
Router Reboot Revival: Sometimes, the solution is simpler than you imagine, like a quick nap to recharge your batteries.
- Unplug your router and modem from the power outlet.
- Wait a full 60 seconds. Yes, count them! This clears the router's memory.
- Plug the modem back in and let it fully boot up.
- Plug the router back in and let it boot up as well.
- Try connecting to the 2.4GHz Wi-Fi again.
Network Name (SSID) Sleuthing:
- Log in to your router's settings (usually through your web browser by typing a specific IP address, like 192.168.1.1, check your router’s manual for the specific address).
- Find the Wi-Fi settings and verify that your 2.4GHz network is visible (not hidden). If your network is hidden, try making it visible.
- If it's already visible, double-check the SSID and that it’s being broadcast.
Channel Configuration Crossroads:
- Within your router settings, look for the Wi-Fi channel settings. The 2.4GHz band uses channels 1-11 (in North America).
- Ideally, select channels 1, 6, or 11. These are the least likely to overlap with neighboring Wi-Fi networks.
- Save the changes and restart your router. This can be a game-changer.
Security Protocol Proficiency:
- In your router’s settings, check the security settings for your 2.4GHz network.
- Make sure the security protocol is set to WPA2-PSK or WPA3 (most modern and secure).
- If you're using WEP, consider switching to a more secure option immediately. WEP is outdated and easily cracked.
Laptop’s Wi-Fi Adapter Adjustments:
- Open Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar).
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Find your Wi-Fi adapter (e.g., Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200).
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Properties."
- Go to the "Advanced" tab.
- Look for a setting related to "Wireless Mode" or "802.11 mode."
- Ensure it’s set to the appropriate mode (e.g., 802.11 b/g/n). Ensure it is not set to a mode your router does not support.
Consider a Factory Reset (Last Resort): Only consider this if all other troubleshooting steps have failed. This wipes your router's settings and restores them to the original state. Make sure you have your internet service provider (ISP) login information handy, because you’ll need it to set up your internet connection.
The Benefits of Reviving the 2.4GHz Connection
Why is it so important to connect to 2.4GHz in the first place? Let’s highlight the advantages.
- Extended Range: 2.4GHz signals penetrate walls and other obstacles better than 5GHz, offering wider coverage, ideal for larger homes or areas with poor reception.
- Device Compatibility: Many older devices still rely on 2.4GHz, making it vital for smart home gadgets, printers, and other technology.
- Less Interference: Although the 2.4GHz band is crowded, sometimes it can have less interference. If you live in an area with many 5GHz networks, 2.4GHz might be the smoother option.
- Reliability: 2.4 GHz can sometimes be more stable in difficult environments, especially if the 5GHz signal is weak or inconsistent.
The 5GHz vs. 2.4GHz Dilemma: Deciding the Best Band
Okay, once you’re up and running, a common question arises: Which band is best? Here’s a simplified comparison:
- 5GHz: Faster speeds, less congested, but shorter range and less penetration. Excellent for streaming, gaming, and data-intensive tasks when you're close to the router.
- 2.4GHz: Slower speeds, longer range, better penetration, more compatible with older devices. Best for general web browsing, email, and devices that don't require super-fast speeds over greater distances.
Ultimately, the "best"
Laptop with BEST WiFi? This SHOCKING Secret Will BLOW Your Mind!Turn OFF 5 GHz WiFi to Connect Smart Devices

By Robert Wilson Turn OFF 5 GHz WiFi to Connect Smart Devices by Robert Wilson
FIX You are sharing your connection over the 5 GHz network band in Windows 10 Unlimited Solutions
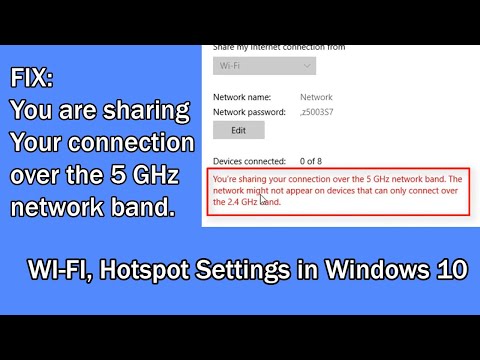
By Unlimited Solutions FIX You are sharing your connection over the 5 GHz network band in Windows 10 Unlimited Solutions by Unlimited Solutions
Can 2.4GHz devices connect to 5GHz

By EntertainmentWHYS Can 2.4GHz devices connect to 5GHz by EntertainmentWHYS

Title: How To Enable 5GHz Wi Fi On Laptop Change Wi-Fi Band From 2.4GHz to 5GHz
Channel: Tweak Library
How To Enable 5GHz Wi Fi On Laptop Change Wi-Fi Band From 2.4GHz to 5GHz by Tweak Library
Wifi Not Found
Laptop Refuses 2.4GHz WiFi? This SHOCKING Fix Works!
The digital world hums with the promise of seamless connectivity, a symphony of data streams orchestrated by our wireless networks. Yet, the idyllic picture often shatters when a laptop, our steadfast companion in this digital ballet, stubbornly refuses to join the 2.4GHz WiFi frequency. This common predicament can transform a productive afternoon into a frustrating scramble. We understand your pain. But fret no more. We've navigated these turbulent waters and emerged with solutions, proven fixes that consistently restore connectivity where it seems lost. Prepare to reclaim your digital freedom.
The 2.4GHz WiFi Conundrum: Understanding the Blockages
Before we dive into the solutions, it's crucial to grasp the underlying reasons why your laptop might be rejecting the 2.4GHz band. This frequency, while offering wider compatibility, is also the victim of overcrowding. Imagine a bustling marketplace; the more vendors vying for attention, the more difficult it is to be heard. Similarly, the 2.4GHz band is often congested with a multitude of devices, including:
- Microwave ovens: These kitchen staples are notorious for interfering with WiFi signals. The radiation they emit operates on the same frequency, creating a digital maelstrom that disrupts your laptop's connection.
- Bluetooth devices: Bluetooth, another ubiquitous technology, also utilizes the 2.4GHz band. Headphones, speakers, and other accessories can contribute to the congestion.
- Cordless phones: Older cordless phones, particularly those operating on the 2.4GHz frequency, can act as potent signal jammers.
- Neighboring WiFi networks: In densely populated areas, numerous WiFi networks compete for the same limited bandwidth, leading to interference and connection issues.
- Physical obstructions: Walls, especially those constructed with dense materials like concrete or brick, can significantly weaken the 2.4GHz signal, hindering your laptop's ability to connect.
Diagnostic Steps: Pinpointing the Root Cause
Before implementing any fixes, a methodical approach is essential. The goal is to identify the specific cause of your laptop's WiFi woes.
- Restart Your Laptop and Router: The classic first step, yet often overlooked. A simple reboot can clear temporary glitches that might be interfering with connectivity. Allow your router a full minute to cycle through its power-up sequence. Then, reboot your laptop.
- Check Your Router's WiFi Settings: Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing its IP address, such as 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, into your web browser; consult your router's documentation if you’re unsure). Scrutinize the WiFi settings. Ensure that the 2.4GHz band is enabled and broadcasting its SSID (network name). Verify the channel the 2.4GHz band is using. Some channels may be more congested than others in your area. Try switching to channels 1, 6, or 11, these are often less crowded.
- Examine Your Laptop's Wireless Network Adapter: Within your laptop's operating system (Windows or macOS), delve into the device manager or network settings. Ensure your wireless network adapter is enabled and functioning correctly. Check for driver updates; outdated or corrupted drivers can be a prime culprit behind connectivity failures.
- Test Other Devices: Attempt to connect other devices (smartphones, tablets, other laptops) to the 2.4GHz network. If these devices connect successfully, the issue likely lies with your specific laptop. If other devices encounter the same problem, the issue is more likely with your router.
- Assess Physical Interference: Move your laptop closer to the router. If the connection improves, physical obstructions are likely the problem. Note the proximity of microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, and other potential sources of interference.
The SHOCKING Fixes That Actually Work
Now, let's explore the solutions, the arsenal of fixes that often resolve the frustrating 2.4GHz WiFi refusal.
1. Channel Surfing: Optimizing Your WiFi Channels
As alluded to earlier, the 2.4GHz band is divided into channels, much like radio frequencies. Just as radio stations can interfere with each other, so can WiFi networks operating on the same channel.
- Channel Selection: Access your router's configuration page and navigate to the wireless settings. Examine the channel settings for the 2.4GHz band. The default setting is often "Auto," which allows the router to select a channel automatically. However, in congested environments, this can lead to suboptimal performance. Manually select a channel: 1, 6, or 11 are often the least congested and therefore the best starting points. Use a WiFi analyzer app (available for smartphones and laptops) to scan the surrounding WiFi networks and identify the least crowded channel in your area.
- Channel Width: Experiment with the channel width. While wider channels offer increased bandwidth (improving speed), they also consume more of the radio spectrum, potentially increasing interference. Try setting the channel width to 20MHz for the 2.4GHz band. This can sometimes alleviate congestion.
2. Firmware Updates: Keeping Your Router’s Brain Sharp
Routers, like laptops, require regular updates. These firmware updates often include bug fixes, security patches, and performance enhancements.
- Check for Updates: Access your router's configuration page and look for a firmware update section. The interface varies by manufacturer, but the update process is generally straightforward. Download and install the latest firmware for your router model. This can often resolve underlying connectivity issues.
- Automated Updates: Some routers offer automated firmware updates. Enable this feature to ensure your router is always running the latest and greatest software.
3. Driver Updates: Bridging the Gap Between Hardware and Software
Your laptop's wireless network adapter relies on drivers, small software programs that allow the operating system to communicate with the hardware. Outdated or corrupted drivers can lead to a breakdown in communication.
- Windows Driver Updates: In Windows, right-click the Start button and select "Device Manager." Expand "Network adapters." Right-click your wireless network adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." If Windows finds new drivers, it will install them. If this fails, try the manufacturer's website for a driver download.
- macOS Driver Considerations: macOS generally handles driver updates automatically. However, if you're experiencing persistent issues, visit the manufacturer's website for your network adapter (or the laptop manufacturer's support page) and manually download and install the latest drivers.
- Reinstalling Drivers: If updating the driver doesn't work, try uninstalling and reinstalling the driver. In Device Manager (Windows), right-click the wireless network adapter, select "Uninstall device," and remove the driver. Restart your laptop, and Windows should automatically reinstall the driver.
4. Router Placement: Strategic Positioning for Optimal Reception
The physical location of your router significantly impacts the strength and range of its WiFi signal.
- Elevated Placement: Place the router in an elevated position (shelf, table) away from the floor. This improves signal propagation, reducing obstructions.
- Central Location: Position the router as close to the center of your home or office as possible. This maximizes coverage, minimizing dead spots.
- Clear Obstructions: Minimize obstructions between the router and your laptop. Remove or relocate objects that could interfere with the signal, such as thick walls, metal objects, and electronic devices.
- Antenna Positioning: Experiment with the router's antenna positioning. Try different angles (vertical, angled) to optimize signal strength.
5. Wireless Security: WPA2/WPA3 Encryption
Ensure your router is using a robust security protocol.
- WPA2 or WPA3: Make sure your router is using WPA2 or WPA3 encryption to secure your wireless network. Older security protocols, like WEP, are easily compromised and can also sometimes cause compatibility issues with modern devices.
- Password Strength: Ensure you have a strong and unique password for your WiFi network.
6. Power Cycling: A Reset for Your Router
Sometimes, a simple reset can resolve stubborn WiFi issues.
- Unplug and Wait: Power cycle your router. Unplug the router from the power outlet. Wait a full minute. Plug it back in. Allow the router to fully boot up before attempting to connect your laptop.
Advanced Troubleshooting: Beyond the Basics
If the basic fixes fail, employ these advanced strategies.
7. Network Adapter Settings: Fine-Tuning for Maximum Performance
- Windows Power Management: In Windows, go to Device Manager, expand "Network adapters," right-click your wireless network adapter, select "Properties," and go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that allows the computer to turn off this device to save power. This can prevent the adapter from entering a low-power state and causing connection problems.
- Network Adapter Configuration: In Windows, in the adapter's properties, look for advanced settings related to wireless modes (802.11n, 802.11g, etc.). Ensure that your adapter is set to support the proper standards. "Mixed mode" is often recommended.
8. Consider a WiFi Extender or Mesh Network
If the issue is coverage, not necessarily interference, consider a WiFi extender or a mesh network
