how to connect wifi in laptop windows 7 manually

Title: How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7
Channel: MDTechVideos International
How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7 by MDTechVideos International
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solve It NOW! (Manual Connection)
Windows 7 WiFi Woes: Conquering the Connection Conundrum (Manual Maneuvers)
Remember those simpler digital days? Back when Windows 7 reigned supreme, and the internet, though still evolving, felt less…complicated? Unfortunately, even then, Wi-Fi wasn't always the seamless experience we craved. Encountering a Windows 7 WiFi nightmare was, unfortunately, not uncommon. But don't despair; there's absolutely a light at the end of the tunnel. This article is geared to help you navigate through those frustrating connection issues. We'll explore the solution: manual connection.
The Ghost in the Machine: Understanding the WiFi Wraith
Before we delve into solutions, however, it's helpful to understand the potential villains. Several factors could be causing that stubborn "no internet" message. Furthermore, it could be a driver issue, a misconfigured network setting, or even a conflict with your router. Sometimes, the problem is just a momentary glitch. Moreover, it might be the wireless adapter in your laptop. Consequently, pinpointing the exact cause requires patience and a systematic approach. Therefore, consider this a digital detective story.
Step-by-Step Symphony: Orchestrating Your Manual Connection
Ready to become a Wi-Fi warrior? Then, let’s get connected! It’s as simple as following this strategic choreography.
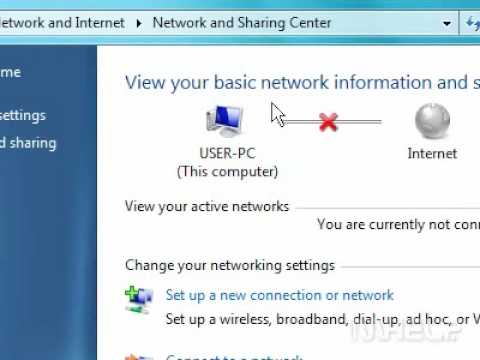
First, you'll need to access your "Network and Sharing Center." Click on the network icon in your system tray (usually down in the bottom right corner). Afterward, select "Open Network and Sharing Center."
Next, click on "Set up a new connection or network."
Subsequently, select "Manually connect to a wireless network" from the options available.
Now, you’ll be prompted to enter details about your wireless network. This is crucial, so pay close attention.
- Network Name (SSID): Type in the exact name of your Wi-Fi network. This is case-sensitive, so double-check.
- Security Type: Choose the appropriate security type. Common options include WPA2-Personal, WPA-Personal, or WEP. If you aren't sure, check your router's settings.
- Encryption Type: Select the encryption type that matches your router's settings. This often aligns with your security type.
- Security Key: Enter your Wi-Fi password (the "network security key") with pinpoint accuracy.
- Start this connection automatically: Check this box if you want Windows 7 to connect automatically the next time it's in range.
- Connect even if the network is not broadcasting: This is useful if your network hides its SSID.
- Lastly, click "Next."
After that, Windows will attempt to connect. If the connection fails, be prepared to troubleshoot.
Troubleshooting Triumphs: Conquering Connection Cave-Ins
So, what happens if the initial setup doesn't work? Don't surrender. Many issues will have simple fixes. Here's a troubleshooting toolkit:
- Double-Check the Basics: Review the entered network name (SSID) and password for any typos. In particular, capitalization matters.
- Router Reboot: Sometimes, the simplest solution is the most effective. Restart your router and modem. Wait a few minutes before trying again.
- Driver Drama: Outdated or corrupt wireless drivers are common culprits. So, visit your laptop manufacturer's website and download the latest drivers for your network adapter. Install them and restart your computer.
- Network Adapter Troubleshooter: Windows 7 has a built-in troubleshooter. Right-click the network icon in your system tray and select "Troubleshoot problems." This can automatically identify and fix many common issues.
- Firewall Follies: Your firewall might be blocking the connection. Temporarily disable your firewall (but re-enable it once you’re up and running) to test. Sometimes, you'll need to create an exception for your wireless adapter.
- IP Address Acquisition: If you’re still struggling, try setting a static IP address. Go to "Network and Sharing Center," then click "Change adapter settings." Right-click on your wireless network and select "Properties." Scroll down and select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)." Click "Properties." Select "Use the following IP address." Enter an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses (you can find these in your router's settings). Afterward, save your changes.
- Consulting the Experts: Eventually, if all else fails, reach out to your internet service provider (ISP) for assistance. They might have specific troubleshooting steps for your connection.
Beyond the Basics: Pro Tips for Persistent Problems
Here are some additional tricks to help you avoid future headaches.
- Keep Your Windows 7 Updated: While Windows 7 support has ended, important security updates might still be relevant. Additionally, ensure you’re running the latest service pack and updates available before the end of support.
- Router Firmware Fortification: Regularly update your router's firmware. This improves performance and security.
- Strategic Router Placement: Ensure your router is centrally located and free from obstructions that can interfere with the signal.
- Wireless Channel Warfare: Experiment with different wireless channels on your router. This can help avoid interference from other networks.
Triumph Over Technology: Your WiFi Victory Lap
Hopefully, armed with these manual connection strategies, you are now back online. Remember, troubleshooting can require patience. However, with a little persistence, you can conquer your Windows 7 WiFi woes. Celebrate your newfound connectivity! You deserve it.
HP 15 Laptop Wi-Fi Nightmare? FIX IT NOW!Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solve It NOW! (Manual Connection)
Hey everyone! Remember those days, staring at a blinking WiFi icon on your Windows 7 machine, feeling like you were stranded on a digital desert island? Yeah, we've all been there. That frustrating feeling of being disconnected when you desperately needed that internet connection! But fear not, because we're diving headfirst into the mucky waters of Windows 7 WiFi woes and, more specifically, conquering them through manual connection. Think of it like learning to tie your shoes – once you get the hang of it, you're unstoppable!
The Phantom WiFi: Why Windows 7 Still Rocks (Sometimes…and Why WiFi Betrays Us)
Let’s be honest, Windows 7, despite its age, still holds a special place in many of our hearts. It's like that reliable old car that, despite its quirks, just works. But the WiFi! Oh, the WiFi! It can be a fickle beast. Why does it sometimes vanish, leaving you staring forlornly at the "No Internet Access" message? Well, there are a multitude of reasons why your Windows 7 machine might be playing hide-and-seek with the internet and we are going to solve this issue today. Here are a couple of common culprits, and many times you'll find a manual connection can save the day!
- Driver Drama: Think of your WiFi drivers as the translators between your computer and the internet. If they're outdated, corrupted, or just plain missing, communication breaks down.
- Network Name Nonsense: You wouldn't believe how often a simple misspelling in the network name can be the issue!
- Router Roulette: Your router might be acting up, dropping the connection like a hot potato.
- Security Shenanigans: Incorrect security key or settings can lock you out of your own network.
- Signal Struggles: Distance and interference can weaken the WiFi signal, making it a ghost connection.
Step One: Grabbing Your Digital Compass – Understanding Your Network
Before we plunge into the manual connection steps, let’s equip ourselves with the right tools. Think of this as assembling your digital compass before heading into the wilderness. We need some key pieces of information:
- Your Network Name (SSID): This is the name your WiFi network broadcasts. It's typically found on your router or in the router's settings.
- Security Type (e.g., WPA2-PSK, WEP): This tells Windows how to encrypt the data transmitted over your network.
- Security Key (Password): This is the password that protects your WiFi network from unwanted guests. Make sure it's not your toddler's birthday, or other easy-to-guess things.
- Optional: IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS Servers: If you're a bit tech-savvy, you might want to make a note of these. You can often find them in your router's settings too. If you are unsure, let windows obtain the IP address automatically, and you can always try to get those settings from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Step Two: The Manual Connection Dance – The Step-by-Step Guide
Alright, here comes the meat of the matter! This is where we actually connect. We're ditching the automatic connection and taking control.
- Click the Network Icon: Look in the bottom-right corner on your system tray (near your clock). It's usually a small icon that looks like a computer screen or a series of bars. Click it.
- Open Network and Sharing Centre: If you want, click "Open Network and Sharing Center".
- Click "Set up a new connection or network": This option is located typically in the “Network and Sharing Center” window.
- Choose "Manually connect to a wireless network": Select this option to set up a new network connection manually.
- Enter Network Information: Now, let's put that compass to good use. A window will pop up asking for:
- Network name: Type your network name (SSID). Be precise!
- Security type: Select the correct security type from the drop-down menu (WPA2-PSK, WEP, etc.)
- Security key: Enter your WiFi password. Double-check this! Typing errors are the most common things.
- Start automatically: Check this box if you want Windows to connect automatically every time you're in range.
- Click "Connect": Windows will attempt to connect to your network. Fingers crossed!
- Troubleshooting – When it Just…Doesn't: If it doesn't work at first, don't panic. Double-check your network name and password. Make sure the security type is correct. If you still have problems, check our troubleshooting tips below!
Step Three: Troubleshooting Time – When the Connection Fails
Sometimes, no matter how careful we are, things still go wrong. Here are some quick fixes for when your Windows 7 is still playing hard to get:
- Double-Check the Basics: Re-enter your network name and password. Spelling and case sensitivity matter!
- Restart Your Router: Unplug your router for 30 seconds and plug it back in. This can often clear up temporary glitches.
- Update Your Drivers: If you have another device connected to the internet, download the latest WiFi drivers for your Windows 7 machine on a USB flash drive. Then, install them on the problematic computer.
- Forget and Reconnect: In network connections, forget the network and then reconnect manually.
- Check the Distance: Are you too far from your router? Walls and other obstacles can weaken the signal. Try moving closer.
Step Four: Hidden Settings and Advanced Tweaks (For the Brave)
Alright, this is for the more adventurous among us. Here are some of the advanced settings to make your connection better:
- IP address settings: Go to the advanced settings and make sure they are configured, and you can always use the "obtain IP address automatically".
- Check network adapter settings: Make sure the network adapter is enabled.
Step Five: Prevent Future WiFi Woes – Proactive Measures
Nobody wants to keep going through this, right? Prevention is better than cure, as they say. Here are some steps to avoid further WiFi nightmares:
- Keep Drivers Updated: Regularly check for and install updated WiFi drivers.
- Strong Passwords: Use a strong, unique password for your WiFi network.
- Restart Regularly: Reboot your router and computer from time to time.
- Placement matters: Position your router for optimal signal coverage.
Windows 7 WiFi – A Retrospective Smile
Look, even with the internet's evolution, the old Windows 7 can still be a joy to use. And sometimes, we just need a quick fix to reconnect. We hope that this guide and the steps above will help you get online faster and get back to enjoying your time! It is not the most convenient of operating systems, but it can work when we take the technical steps!
FAQs - Your Burning Questions Answered!
1. Why won't my Windows 7 laptop connect to WiFi automatically?
There are various reasons: incorrect password, corrupted drivers, or a problem with the router's settings. Recheck your credentials, update your drivers, and restart your router if needed.
2. I can see my network, but can't connect. What's wrong?
Most often, an incorrect password or security key is the problem. Otherwise, try restarting your router or updating your network driver.
3. Is manually connecting more secure than automatically connecting?
No, the security lies in the encryption type (e.g., WPA2) and your chosen password, not how you connect.
4. My internet is slow! Is it still a WiFi problem?
Possibly. Consider your internet plan, your distance from the router, and any possible interference. Also, test the speed of your connection with an online speed test such as Speedtest by Ookla.
5. Can I use a wired (Ethernet) connection instead?
Absolutely! A wired connection offers the best possible speeds and stability. If your device has an Ethernet port, it is a great alternative to WiFi.
Conclusion: Embracing the Manual Connection and Beyond
So, there you have it! We've navigated the treacherous waters of Windows 7 WiFi, armed with the power of manual connection. Remember, technical woes can be like puzzles, and with a bit of patience and the right steps, we can always solve them. We can always try again! Now go forth, reconnect, and enjoy!
- Principal Keywords: Windows 7 WiFi Manual Connect Troubleshoot.
- SEO Headline: Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Fix It! Manual Connection Guide
- Pathway: Windows 7 WiFi
- Meta Summary: Windows 7 WiFi problems? Learn to connect manually & troubleshoot WiFi issues. Solve your Windows 7 WiFi nightmare NOW! A step-by-step guide.
- Image Alt Text: Windows 7 showing a manual network connection, with a frustrated user.
How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U
CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7

By Rdn Channel CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7 by Rdn Channel
Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop

By IT Magics Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop by IT Magics

Title: Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011
Channel: inprez id
Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011 by inprez id
Laptop Working
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solve It NOW! (Manual Connection)
Navigating the digital realm should be a seamless experience, a fluid connection to information and communication. Yet, for countless users of Windows 7, the specter of a malfunctioning Wi-Fi connection has haunted their online endeavors. The frustrating reality of disappearing signals, intermittent connectivity, and outright refusal to connect can transform a simple task into a protracted battle. But fear not! This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to conquer your Windows 7 Wi-Fi woes, focusing, specifically, on the power of manual connection. Prepare to reclaim your digital freedom and banish those connection frustrations once and for all.
Understanding the Core Issue: Why is my Windows 7 Wi-Fi acting up?
Before we delve into solutions, it’s helpful to grasp the common culprits behind Wi-Fi connection malfunctions on Windows 7. While the reasons are diverse, we can categorize them to provide a clearer path to resolution. Hardware related issues are a common problem. Faulty network adapters, problematic routers, and external interference constitute one group. Another prominent category encompasses software conflicts. These can include outdated or corrupt network drivers, interference from firewalls, or incorrect network settings. Finally, environmental factors, such as distance from the router or obstructions in the signal path, can also play a significant role. Grasping that these factors are often intertwined is critical to successful troubleshooting.
Section 1: Verifying the Basics – Is the Problem Really Your Computer?
Sometimes, the simplest checks are the most effective. Before embarking on complex troubleshooting, ensure that the issue truly lies within your Windows 7 system and not elsewhere.
The Router Reboot: The primary step is a router reboot. Unplug your router from the power outlet, wait approximately 30 seconds, and plug it back in. Allow the router ample time to restart, typically a couple of minutes. This simple reset resolves a significant percentage of connection issues by clearing temporary glitches within the router's firmware.
Other Devices Test: Does your Wi-Fi work with other devices? Test your connection on smartphones, tablets, or other computers. If these devices connect without issue, you can focus troubleshooting on your Windows 7 machine. If other devices fail to connect either, the problem is likely your router or your internet service provider.
Physical Inspection: Verify the physical connection between your computer and the router. Ensure any Ethernet cables are securely connected if the issue is with a wired connection.
Section 2: Manual Connection: The Direct Route to a Stable Wi-Fi Signal
Windows 7, despite its age, provides robust tools for manually configuring Wi-Fi connections, offering a level of control that can bypass many common problems. This method empowers you to directly engage with your network settings, bypassing potential issues related to automatic configuration.
Accessing the Network and Sharing Center: The control hub for network settings is the first stop on our journey. Navigate to the Control Panel, and then select "Network and Internet." From there, click on "Network and Sharing Center." This central point allows you to manage your network connections and access settings.
Manually Adding a Wireless Network Profile: In the Network and Sharing Center, look for the option "Set up a new connection or network." This option initiates the process of creating a new network profile. Choose "Manually connect to a wireless network" from the subsequent options.
Inputting Network Details: The next step involves entering your wireless network credentials. You will need the following information:
- Network Name (SSID): This is the name of your Wi-Fi network, usually printed on your router or in its configuration settings. Ensure you enter it exactly as it appears, paying attention to capitalization and spacing.
- Security Type: This specifies the security protocol your network uses. Common options include WPA2-PSK (AES), WPA-PSK (TKIP), and WEP. Choose whichever security protocol is supported by your router. WPA2-PSK (AES) is generally the most secure and recommended option.
- Security Key (Password): This is the password for your Wi-Fi network. Enter it carefully, ensuring that it matches your router's security settings.
Advanced Settings (If Necessary): Click the "Change connection settings" checkbox, and then navigate to the "Security" tab. If your Wi-Fi requires additional settings, such as a specific authentication method or encryption algorithm, those configurations can be adjusted here.
Saving and Connecting: Click "OK" to save your network profile. Windows 7 will then attempt to connect to your chosen network. If the credentials are correct, you should connect to your network.
Section 3: Driver Updates – Ensuring Compatibility and Performance
Outdated or corrupted network drivers are a prevalent cause of Wi-Fi connection issues. Keeping your network drivers up-to-date is essential for optimal performance and compatibility. This process involves identifying your network adapter and updating its drivers.
Identifying Your Network Adapter: Before updating, you must know your network adapter model. Right-click on "Computer" on your desktop or in the Start menu, and select "Manage." In the Computer Management window, navigate to "Device Manager" on the left panel. Expand the "Network adapters" section. You will see a list of network adapters installed on your system. Often, the adapter name will include "Wireless," "Wi-Fi," or similar terminology.
Updating Drivers Through Device Manager: Right-click on your wireless network adapter in Device Manager and select "Update driver software…" Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows 7 will search for the latest drivers online and install them if available.
Manual Driver Update (If Automatic Update Fails): If the automatic method fails to locate newer drivers, you'll need to search for them manually. Visit the website of your computer manufacturer (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) or the network adapter manufacturer (e.g., Intel, Broadcom). Search for the driver for your specific adapter model and Windows 7. Download and install the driver package.
Restart Your Computer: After a driver update, restart your computer to allow the new driver to take effect. This final action often resolves driver-related connectivity problems.
Section 4: Troubleshooting Common Connectivity Roadblocks
Even with the above steps, problems may persist. This section addresses common hurdles and provides solutions to overcome them.
Incorrect Security Key: Double-check the security key you entered during the manual connection setup. Ensure the capitalization, spacing, and all characters align precisely with your router's configuration. A single character error will prevent connection.
Router Channel Congestion: Wi-Fi routers broadcast on channels. If your network is situated on a congested channel, interference can occur. Access your router’s settings (usually through a web browser by entering your router’s IP address) and experiment with different Wi-Fi channels. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are generally less crowded. Experiment to find the optimal channel.
Firewall Interference: Your computer's firewall, or a third-party firewall, can sometimes block Wi-Fi connections. Temporarily disable your firewall (ensuring you know how to re-enable it), and test your Wi-Fi. If disabling the firewall resolves the issue, you need to adjust the firewall settings to allow Wi-Fi traffic. Consult your firewall's documentation for specific configuration instructions.
Network Adapter Power Management: Your network adapter's power management settings can inadvertently disrupt your connection. In Device Manager (as described earlier), right-click your network adapter and select "Properties." Navigate to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This setting can prevent your adapter from going into a low-power mode, which can lead to connection issues.
Windows Network Troubleshooter Last Resort: Windows 7 has a built-in Network Troubleshooter. You can access it through the Network and Sharing Center. It is not always successful but worth a try. Click on "Troubleshoot problems" to automatically scan and diagnose potential network issues.
Section 5: Advanced Techniques for Persistent Problems
If the preceding measures fail, these more advanced techniques can provide further resolution.
Resetting TCP/IP Stack and Winsock: Network settings sometimes become corrupted. You can reset the TCP/IP stack and Winsock, which manage network communication. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator (search for "cmd" in the Start menu, right-click the icon, and then select "Run as administrator"). Enter the following commands, pressing Enter after each line:
netsh winsock reset netsh int ip reset ipconfig /flushdnsRestart your computer after executing these commands.
Reinstalling the Network Adapter: If driver updates, resetting the TCP/IP stack, and all else have failed, consider reinstalling the network adapter. In Device Manager, right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Uninstall." Restart your computer and Windows 7 will automatically reinstall the adapter.
Router Firmware Update: Router firmware, like network card drivers, becomes outdated. An update improves performance and fixes bugs. Access your router's configuration, usually by entering its IP address in a web browser. Find the firmware update feature, download the update from the manufacturer's website, and install it.
Section 6: Preventing Future Wi-Fi Headaches
Proactive measures can help prevent recurring Wi-Fi problems.
- **Regular
